from pynucastro.nucdata import Nucleus
from pynucastro.rates.rate import Rate
[docs]
def create_double_neutron_capture(lib, reactant, product):
"""A helper function that will return a pair of
:py:class:`ApproximateRate` objects for the A(n,g)X(n,g)B ->
A(nn,g)B approximation
Parameters
----------
lib : Library
A Library object containing the neutron-capture rates
reactant : Nucleus, str
The reactant, A, in the sequence A(n,g)X(n,g)B
product: Nucleus, str
The product, B, in the sequence A(n,g)X(n,g)B
Returns
-------
ApproximateRate, ApproximateRate
"""
if isinstance(reactant, str):
reactant = Nucleus(reactant)
if isinstance(product, str):
product = Nucleus(product)
intermediate = reactant + Nucleus("n")
forward_1 = lib.get_rate_by_name(f"{reactant.raw}(n,){intermediate.raw}")
forward_2 = lib.get_rate_by_name(f"{intermediate.raw}(n,){product.raw}")
reverse_1 = lib.get_rate_by_name(f"{product.raw}(,n){intermediate.raw}")
reverse_2 = lib.get_rate_by_name(f"{intermediate.raw}(,n){reactant.raw}")
forward = ApproximateRate(None, [forward_1, forward_2],
None, [reverse_1, reverse_2],
approx_type="nn_g",
use_identical_particle_factor=False)
reverse = ApproximateRate(None, [forward_1, forward_2],
None, [reverse_1, reverse_2],
approx_type="nn_g", is_reverse=True,
use_identical_particle_factor=False)
return forward, reverse
[docs]
class ApproximateRate(Rate):
"""An approximation to a rate sequence. Two approximations are
currently supported:
* "ap_pg" : combine the A(a, g)B and A(a, p)X(p, g)B sequences
into a single, effective A(a, g)B rate.
* "nn_g" : replace the sequence A(n, g)X(n, g)B with an
effective A(nn, g)B rate.
This class stores all of the rates needed to implement these
approximations.
Parameters
----------
primary_rate : Rate
An existing rate that represents the same sequence as the
approximation we are creating. For "ap_pg", this would be
A(a, g)B. For "nn_g", there is no unapproximated counterpart
so we would pass in ``None``.
secondary_rates : list(Rate)
A list of :py:class:`Rate <pynucastro.rates.rate.Rate>` objects
containing all of the other forward rates needed to make the
approximation.
primary_reverse : Rate
An existing rate that represents the reverse of the same
approximation we are creating. For "ap_pg", this would be
B(g, a)A. For "nn_g", there is no unapproximated counterpart,
so we would pass in ``None``.
secondary_reverse : list(Rate)
A list of :py:class:`Rate <pynucastro.rates.rate.Rate>` objects
containing all of the other reverse rates needed to make the
approximation.
is_reverse : bool
Are we creating the effective A(x,y)B or B(y, x)A?
approx_type : str
The type of approximation to do. Currently supported are
"ap_pg" and "nn_g"
use_identical_particle_factor : bool
Usually if a rate has 2 reactants of the same type, we
divide by 2, since the order doesn't matter. However, for
some approximations, like A(n,g)X(n,g)B -> A(nn,g), we
don't want this factor, since the neutron captures are
sequential. This option allows the double counting
factor to be disabled.
"""
def __init__(self, primary_rate, secondary_rates,
primary_reverse, secondary_reverse, *,
is_reverse=False, approx_type="ap_pg",
use_identical_particle_factor=True):
# this will hold all of the rates
self.rates = {}
# this will hold only those rates that are approximated out. This is
# used primarily for the RateCollection plot()
self.hidden_rates = []
self.is_reverse = is_reverse
self.approx_type = approx_type
# some approximate rates will require density or composition,
# so when we output the python or C++ function, we will need
# these in the argument list.
self.rate_eval_needs_rho = False
self.rate_eval_needs_comp = False
if self.approx_type == "ap_pg":
# an ap_pg approximate rate combines A(a,g)B and A(a,p)X(p,g)B into a
# single effective rate by assuming proton equilibrium.
assert len(secondary_rates) == 2
# make sure that the primary forward rate makes sense
# this should be A(a,g)B
assert Nucleus("he4") in primary_rate.reactants and len(primary_rate.products) == 1
self.rates["A(a,g)B"] = primary_rate
# we are going to define the product A and reactant B from this reaction
self.primary_reactant = max(primary_rate.reactants)
self.primary_product = max(primary_rate.products)
# the first secondary rate should be A(a,p)X, where X is the
# intermediate nucleus
assert (self.primary_reactant in secondary_rates[0].reactants and
Nucleus("he4") in secondary_rates[0].reactants and
Nucleus("p") in secondary_rates[0].products)
self.rates["A(a,p)X"] = secondary_rates[0]
# the intermediate nucleus is not in our network, so make it
# dummy
self.intermediate_nucleus = max(secondary_rates[0].products)
# now the second secondary rate show be X(p,g)B
assert (self.intermediate_nucleus in secondary_rates[1].reactants and
Nucleus("p") in secondary_rates[1].reactants and
self.primary_product in secondary_rates[1].products)
self.rates["X(p,g)B"] = secondary_rates[1]
# now ensure that the reverse rate makes sense
# the primary reverse rate is B(g,a)A
assert (self.primary_product in primary_reverse.reactants and
self.primary_reactant in primary_reverse.products)
self.rates["B(g,a)A"] = primary_reverse
# now the first secondary reverse rate should be B(g,p)X
assert (self.primary_product in secondary_reverse[0].reactants and
self.intermediate_nucleus in secondary_reverse[0].products and
Nucleus("p") in secondary_reverse[0].products)
self.rates["B(g,p)X"] = secondary_reverse[0]
# and the second secondary reverse rate should be X(p,a)A
assert (self.intermediate_nucleus in secondary_reverse[1].reactants and
Nucleus("p") in secondary_reverse[1].reactants and
self.primary_reactant in secondary_reverse[1].products and
Nucleus("he4") in secondary_reverse[1].products)
self.rates["X(p,a)A"] = secondary_reverse[1]
# now initialize the super class with these reactants and products
if not self.is_reverse:
super().__init__(reactants=[self.primary_reactant, Nucleus("he4")],
products=[self.primary_product],
label="approx",
use_identical_particle_factor=use_identical_particle_factor)
else:
super().__init__(reactants=[self.primary_product],
products=[self.primary_reactant, Nucleus("he4")],
label="approx",
use_identical_particle_factor=use_identical_particle_factor)
self.chapter = "a"
self.hidden_rates = [self.rates["A(a,p)X"],
self.rates["X(p,g)B"],
self.rates["B(g,p)X"],
self.rates["X(p,a)A"]]
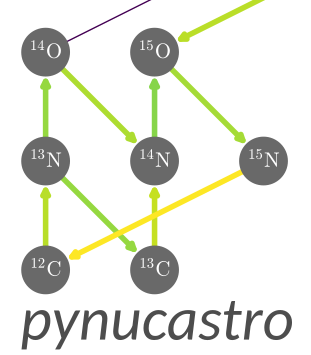
elif self.approx_type == "nn_g":
# a nn_g approximate rate combines A(n,g)X(n,g)B into a
# single effective rate by assuming equilibrium of X.
assert primary_rate is None
assert len(secondary_rates) == 2
# make sure that the pair of forward secondary makes sense
# the first secondary rate should be A(n,g)X and the
# second should be X(n,g)B
for rr in secondary_rates:
assert Nucleus("n") in rr.reactants and len(rr.products) == 1
# make sure that the intermediate nucleus matches
assert secondary_rates[0].products[0] == max(secondary_rates[1].reactants)
# we are going to define the product A and reactant B from
# these forward secondary rates
self.primary_reactant = max(secondary_rates[0].reactants)
self.primary_product = max(secondary_rates[1].products)
self.rates["A(n,g)X"] = secondary_rates[0]
self.rates["X(n,g)B"] = secondary_rates[1]
# the intermediate nucleus is not in our network, so make it
# dummy
self.intermediate_nucleus = max(secondary_rates[0].products)
# now ensure that the reverse rates makes sense
assert primary_reverse is None
assert len(secondary_reverse) == 2
for rr in secondary_reverse:
assert len(rr.reactants) == 1
# now the first secondary reverse rate should be B(g,n)X
assert (self.primary_product in secondary_reverse[0].reactants and
self.intermediate_nucleus in secondary_reverse[0].products and
Nucleus("n") in secondary_reverse[0].products)
self.rates["B(g,n)X"] = secondary_reverse[0]
# and the second secondary reverse rate should be X(g,n)A
assert (self.intermediate_nucleus in secondary_reverse[1].reactants and
self.primary_reactant in secondary_reverse[1].products and
Nucleus("n") in secondary_reverse[1].products)
self.rates["X(g,n)A"] = secondary_reverse[1]
# now initialize the super class with these reactants and products
if not self.is_reverse:
super().__init__(reactants=[self.primary_reactant, Nucleus("n"), Nucleus("n")],
products=[self.primary_product],
label="approx",
use_identical_particle_factor=use_identical_particle_factor)
else:
super().__init__(reactants=[self.primary_product],
products=[self.primary_reactant, Nucleus("n"), Nucleus("n")],
label="approx",
use_identical_particle_factor=use_identical_particle_factor)
self.chapter = "a"
# none of these rates directly appear as links in the network
self.hidden_rates = list(self.rates.values())
self.rate_eval_needs_rho = True
self.rate_eval_needs_comp = True
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"approximation type {self.approx_type} not supported")
# update the Q value
self._set_q()
[docs]
def get_child_rates(self):
"""Return a list of all of the rates that are used in this
approximation.
Returns
-------
list(Rate)
"""
return list(self.rates.values())
def _set_screening(self):
# the individual rates are screened -- we don't screen the combination of them
pass
[docs]
def eval(self, T, *, rho=None, comp=None):
"""Evaluate the approximate rate.
Parameters
----------
T : float
the temperature to evaluate the rate at
rho : float
the density to evaluate the rate at
comp : Composition
the composition to evaluate the rate with
Returns
-------
float
"""
if self.approx_type == "ap_pg":
if not self.is_reverse: # pylint: disable=no-else-return
# the approximate forward rate is r_ag + r_ap r_pg / (r_pg + r_pa)
r_ag = self.rates["A(a,g)B"].eval(T)
r_ap = self.rates["A(a,p)X"].eval(T)
r_pg = self.rates["X(p,g)B"].eval(T)
r_pa = self.rates["X(p,a)A"].eval(T)
return r_ag + r_ap * r_pg / (r_pg + r_pa)
else:
# the approximate reverse rate is r_ga + r_pa r_gp / (r_pg + r_pa)
r_ga = self.rates["B(g,a)A"].eval(T)
r_gp = self.rates["B(g,p)X"].eval(T)
r_pa = self.rates["X(p,a)A"].eval(T)
r_pg = self.rates["X(p,g)B"].eval(T)
return r_ga + r_pa * r_gp / (r_pg + r_pa)
elif self.approx_type == "nn_g":
# we are approximating A(n,g)X(n,g)B
Yn = comp.get_molar()[Nucleus("n")]
if not self.is_reverse: # pylint: disable=no-else-return
# the forward rate
A_ng_X = self.rates["A(n,g)X"].eval(T)
X_ng_B = self.rates["X(n,g)B"].eval(T)
X_gn_A = self.rates["X(g,n)A"].eval(T)
return A_ng_X * X_ng_B / (rho * Yn * X_ng_B + X_gn_A)
else:
# the reverse rate
B_gn_X = self.rates["B(g,n)X"].eval(T)
X_gn_A = self.rates["X(g,n)A"].eval(T)
X_ng_B = self.rates["X(n,g)B"].eval(T)
return B_gn_X * X_gn_A / (rho * Yn * X_ng_B + X_gn_A)
raise NotImplementedError(f"approximation type {self.approx_type} not supported")
[docs]
def function_string_py(self):
"""Return a string containing the python function that
computes the approximate rate.
Returns
-------
str
"""
if self.approx_type == "ap_pg":
# we are approximating A(a,p)X(p,g)B
string = ""
string += "@numba.njit()\n"
string += f"def {self.fname}(rate_eval, tf):\n"
if not self.is_reverse:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
string += f" r_ag = rate_eval.{self.rates['A(a,g)B'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_ap = rate_eval.{self.rates['A(a,p)X'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_pg = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_pa = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].fname}\n"
# now the approximation
string += " rate = r_ag + r_ap * r_pg / (r_pg + r_pa)\n"
else:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
string += f" r_ga = rate_eval.{self.rates['B(g,a)A'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_pa = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_gp = rate_eval.{self.rates['B(g,p)X'].fname}\n"
string += f" r_pg = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].fname}\n"
# now the approximation
string += " rate = r_ga + r_pa * r_gp / (r_pg + r_pa)\n"
string += f" rate_eval.{self.fname} = rate\n\n"
return string
if self.approx_type == "nn_g":
# we are approximating A(n,g)X(n,g)B
string = ""
string += "@numba.njit()\n"
string += f"def {self.fname}(rate_eval, tf, rho=None, Y=None):\n"
string += " Yn = Y[jn]\n"
if not self.is_reverse:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
string += f" r1_ng = rate_eval.{self.rates['A(n,g)X'].fname}\n"
string += f" r2_ng = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].fname}\n"
string += f" r1_gn = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].fname}\n"
# now the approximation
string += " rate = r1_ng * r2_ng / (rho * Yn * r2_ng + r1_gn)\n"
else:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
string += f" r1_gn = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].fname}\n"
string += f" r2_gn = rate_eval.{self.rates['B(g,n)X'].fname}\n"
string += f" r2_ng = rate_eval.{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].fname}\n"
# now the approximation
string += " rate = r1_gn * r2_gn / (rho * Yn * r2_ng + r1_gn)\n"
string += f" rate_eval.{self.fname} = rate\n\n"
return string
raise NotImplementedError("don't know how to work with this approximation")
[docs]
def function_string_cxx(self, dtype="double", specifiers="inline",
leave_open=False, extra_args=None):
"""Return a string containing the C++ function that computes
the approximate rate
Parameters
----------
dtype : str
The C++ datatype to use for all declarations
specifiers : str
C++ specifiers to add before each function declaration
(i.e. "inline")
leave_open : bool
If ``true``, then we leave the function unclosed (no "}"
at the end). This can allow additional functions to add
to this output.
extra_args : list(str)
A list of strings representing additional arguments that
should be appended to the argument list when defining the
function interface.
Returns
-------
str
"""
if extra_args is None:
extra_args = ()
if dtype == "amrex::Real":
array_type = "amrex::Array1D"
else:
array_type = "Array1D"
if self.approx_type == "ap_pg":
args = ["const T& rate_eval", f"{dtype}& rate", f"{dtype}& drate_dT", *extra_args]
fstring = ""
fstring = "template <typename T>\n"
fstring += f"{specifiers}\n"
fstring += f"void rate_{self.cname()}({', '.join(args)}) {{\n\n"
if not self.is_reverse:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
fstring += f" {dtype} r_ag = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['A(a,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_ap = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['A(a,p)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_pg = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_pa = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].cname()});\n"
# now the approximation
fstring += f" {dtype} dd = 1.0_rt / (r_pg + r_pa);\n"
fstring += " rate = r_ag + r_ap * r_pg * dd;\n"
fstring += " if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, rate_derivs_t>) {\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_ag = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['A(a,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_ap = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['A(a,p)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_pg = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_pa = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += " drate_dT = drdT_ag + drdT_ap * r_pg * dd + r_ap * drdT_pg * dd - r_ap * r_pg * dd * dd * (drdT_pg + drdT_pa);\n"
fstring += " }\n"
else:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
fstring += f" {dtype} r_ga = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['B(g,a)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_pa = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_gp = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['B(g,p)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r_pg = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].cname()});\n"
# now the approximation
fstring += f" {dtype} dd = 1.0_rt / (r_pg + r_pa);\n"
fstring += " rate = r_ga + r_gp * r_pa * dd;\n"
fstring += " if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, rate_derivs_t>) {\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_ga = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['B(g,a)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_pa = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(p,a)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_gp = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['B(g,p)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} drdT_pg = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(p,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += " drate_dT = drdT_ga + drdT_gp * r_pa * dd + r_gp * drdT_pa * dd - r_gp * r_pa * dd * dd * (drdT_pg + drdT_pa);\n"
fstring += " }\n"
if not leave_open:
fstring += "}\n\n"
return fstring
if self.approx_type == "nn_g":
args = ["const T& rate_eval", f"const {dtype} rho", f"const {array_type}<{dtype}, 1, NumSpec>& Y",
f"{dtype}& rate", f"{dtype}& drate_dT", *extra_args]
fstring = ""
fstring = "template <typename T>\n"
fstring += f"{specifiers}\n"
fstring += f"void rate_{self.cname()}({', '.join(args)}) {{\n\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} Yn = Y(N);\n"
if not self.is_reverse:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
fstring += f" {dtype} r1_ng = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['A(n,g)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r2_ng = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r1_gn = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].cname()});\n"
# now the approximation
fstring += f" {dtype} dd = 1.0_rt / (rho * Yn * r2_ng + r1_gn);\n"
fstring += " rate = r1_ng * r2_ng * dd;\n"
fstring += " if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, rate_derivs_t>) {\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr1dT_ng = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['A(n,g)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr2dT_ng = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr1dT_gn = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += " drate_dT = dr1dT_ng * r2_ng * dd + r1_ng * dr2dT_ng * dd - r1_ng * r2_ng * dd * dd * (rho * Yn * dr2dT_ng + dr1dT_gn);\n"
fstring += " }\n"
else:
# first we need to get all of the rates that make this up
fstring += f" {dtype} r1_gn = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r2_gn = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['B(g,n)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} r2_ng = rate_eval.screened_rates(k_{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].cname()});\n"
# now the approximation
fstring += f" {dtype} dd = 1.0_rt / (rho * Yn * r2_ng + r1_gn);\n"
fstring += " rate = r1_gn * r2_gn * dd;\n"
fstring += " if constexpr (std::is_same_v<T, rate_derivs_t>) {\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr1dT_gn = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(g,n)A'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr2dT_gn = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['B(g,n)X'].cname()});\n"
fstring += f" {dtype} dr2dT_ng = rate_eval.dscreened_rates_dT(k_{self.rates['X(n,g)B'].cname()});\n"
fstring += " drate_dT = dr1dT_gn * r2_gn * dd + r1_gn * dr2dT_gn * dd - r1_gn * r2_gn * dd * dd * (rho * Yn * dr2dT_ng + dr1dT_gn);\n"
fstring += " }\n"
if not leave_open:
fstring += "}\n\n"
return fstring
raise NotImplementedError("don't know how to work with this approximation")